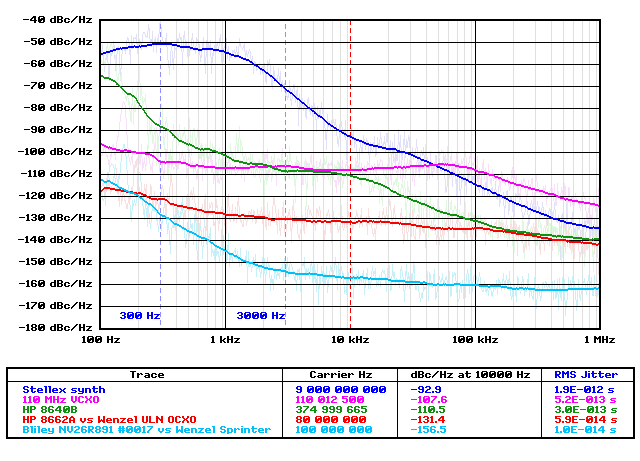
User-Friendly Phase-Noise Measurement for HP, Tektronix and Advantest Spectrum Analyzers
PN.EXE is a graphical Win32 application that lets you acquire, display, overlay, caption, and print noise plot (.PNP) files. It offers many of the capabilities provided by Agilent�s 85671A phase-noise measurement package.
The current version of PN supports the following spectrum analyzer models:
- Tektronix 490P/2750P series
- Tektronix 2782/2784
- HP 8566/8567/8568 series (both -A and -B models)
- HP 8560A/8560E/8590-series portables
- HP 70000 series
- HP 3585A/B
- HP 3588A/3589A
- HP 4195A
- HP 4396A/B
- Advantest R3131
- Advantest R3132, R3162, R3172, and R3182
- Advantest R3264, R3267, and R3273
- Advantest R3463, R3465, R3263, and R3272
- Advantest R3261, R3361, R3265, and R3271
- Advantest TR417x series
- Agilent E4400 ESA/PSA series
- Agilent E4406A VSA
- Rohde & Schwarz FSE series and FSIQ
- Anritsu MS8604A
PN is able to support the �classic� models like the HP 8566 because it runs on a GPIB-connected host PC, rather than the analyzer's own internal processor. Even when running on an $83,000 HP 8565EC, the Agilent noise-measurement software can�t take advantage of the control, display, and connectivity options available on a modern PC.
PN.EXE is part of the KE5FX GPIB Toolkit. The latest version of the Toolkit is downloadable here.
Prerequisites
Although PN is very easy to use, the art of making valid, repeatable noise measurements demands an understanding of the limitations of the instruments and processes involved. HP application note AN 270-2 is strongly recommended to users who are new to PN and phase-noise measurement in general. Don't be put off by its focus on a particular analyzer -- this is the best app note on the subject that I've seen.
For more information, see Hewlett-Packard's Phase Noise Measurement Seminar course notes (124 pages, 7 MB), as well as the other references mentioned in the GPIB Toolkit FAQ.
Running PN
Depending on the options you selected during installation, you can run PN.EXE from the Start menu, by clicking on its desktop shortcut, or by using its Quick Launch icon on the taskbar. You can also run PN.EXE from a DOS-box command line or Windows Start->Run... command, optionally specifying the filenames of one or more existing .PNP files. Use quotes around filenames that contain spaces -- for example,
PN "synth test.pnp" ... Display "synth test.pnp" by itself
PN before.pnp after.pnp ... Overlay before.pnp and after.pnp
PN (no command-line options) ... Attempt to reload the last-viewed set of .PNP files, if any
Menu Commands and Keyboard Shortcuts
Note that many of the menu commands in PN have equivalent keyboard shortcuts, useful on crowded lab benches that don�t have room for a mouse.
Key Menu Command Remarks
l File->Load PNP data... Load and display a new .PNP file. Up to 8 acquisitions may be loaded at once
s File->Save image or PNP data... Save a .GIF, .TGA, .BMP, or .PCX, or a copy of the currently selected .PNP file
x File->Export smoothed trace to .TXT or .CSV file
Save the currently selected trace as a list of comma-separated
offset (Hz), amplitude (dBc/Hz) pairs. If the .TXT suffix is used,
each offset,amplitude pair will be followed by a CR/LF
p File->Print image Sends the current display to the default Windows printer
File->Sort file dialogs by modification date
Causes file listings to be sorted by modification date by default, rather than
by filename
Delete File->Close current plot Remove current .PNP file from display list, without deleting it
Home File->Close all visible plots Close all loaded .PNP files. This command does not delete
any files; it simply removes them from PN.EXE's current display list.
Ctrl-Delete File->Delete current .PNP file Remove current .PNP file from display list, deleting it permanently
q or Esc File->Quit
b View->Browse sources one at a time Surf through all loaded .PNP files without overlaying them
o View->Overlay all sources Display up to eight .PNP files at once
+ or down-arrow View->Next source Advance selection to the next .PNP file
- or up-arrow View->Previous source Go back to the previous .PNP file
Ctrl-up-arrow View->Move selected source up Move selection up in the list of loaded .PNP files
Ctrl-down-arrow View->Move selected source down Move selection down in the list of loaded .PNP files
v View->Toggle visibility of selected source
Allows you to temporarily remove a trace from the
display without closing it; useful when comparing
traces in displays with numerous overlaid sources
5 Display->512 x 384 Adjust window area to one of several standard sizes
6 Display->640 x 480 (These commands are particularly useful when you�ve
7 Display->800 x 600 selected too many entries with the Legend menu,
8 Display->1024 x 768 causing the table to grow beyond the confines of the
9 Display->1152 x 864 window)
0 Display->1280 x 1024
C Display->High contrast Toggle between low-contrast and high-contrast display modes for best
legibility on various displays and printers
Ctrl-0 Trace->No smoothing No smoothing is applied to the visible trace(s)
Ctrl-1 Trace->2-point smoothing Smooth by averaging the specified number of adjacent trace points
Ctrl-2 Trace->4-point smoothing at each pixel
Ctrl-3 Trace->8-point smoothing
Ctrl-4 Trace->16-point smoothing
Ctrl-5 Trace->24-point smoothing
Ctrl-6 Trace->32-point smoothing
Ctrl-7 Trace->48-point smoothing
Ctrl-8 Trace->64-point smoothing
Ctrl-9 Trace->96-point smoothing
Trace->Use alternate smoothing algorithm
Selects a different smoothing technique that provides greater
accuracy at the traces' left endpoint in certain situations
Ctrl-s Trace->Enable spur reduction Helps reduce the influence of discrete spurs on traces,
at some cost in rendering speed
t Trace->Set spur threshold in dB... Allows you to specify the spur-detection threshold relative to
the average value of nearby trace points. You can also
use ctrl-keypad- and ctrl-keypad+ to increment and decrement
the threshold while observing its effect on the displayed traces.
Excessive use of spur clipping will degrade overall accuracy!
g Trace->Enable ghosting Show or hide unsmoothed raw trace(s) behind smoothed trace(s)
c Trace->Allow vertical clipping Attempt to improve the legibility of traces by giving them more
vertical headroom
e Trace->Edit caption... Change or add a caption for the currently-selected trace
The trace's file will be updated automatically with the new caption
Legend->Trace Display trace caption
Legend->Filename Display trace filename
Legend->Carrier Hz Display frequency of carrier from which trace was acquired
Legend->Carrier dBm Display amplitude of carrier from which trace was acquired
Legend->dBc/Hz at Spot Offset Display trace amplitude at spot on graph selected via left click
Legend->Residual FM Hz Display DSB residual-FM amplitude between the integration cursors
Legend->RMS Integrated Noise (Degs) Display DSB RMS phase jitter in degrees or radians for the area between
Legend->RMS Integrated Noise (Rads) the integration cursors
Legend->RMS Time Jitter Display the same phase-jitter value in seconds, based on the carrier frequency
Legend->SSB Carrier/Noise dB Dislpay SSB power between the integration cursors, relative to the carrier level
Legend->Ext Mult Display external frequency multiplication factor, if any
Legend->Ext LO Display frequency of external LO, if any
Legend->Ext IF Display frequency of external IF, if any
Legend->RF Atten dB Display analyzer�s RF attenuator setting
Legend->Clip dB Display requested carrier-clipping value in dB
Legend->VBW/RBW Display video/resolution bandwidth ratio
Legend->Sweep Display total time taken by all sweeps during acquisition
Legend->Time/Date Display acquisition time/date stamp
Legend->Instrument Display spectrum-analyzer model designator
Legend->Rev Display spectrum-analyzer revision designator
Legend->All Select all displayable fields above
Legend->None Deselect all displayable fields above
Acquire-> ... Acquire noise plot from various spectrum analyzer models
Space Acquire->Repeat last acquisition ... Shortcut to return to most-recently-used acquisition dialog
Mouse Controls and Integration Features
Left-click anywhere within the graph to place the red "Spot Cursor" at the nearest vertical division. This cursor will be visible only if the Legend->dBc/Hz at Spot Offset option is selected for viewing.
Ctrl-left click within the graph to establish the lower integration-range offset for the Residual FM Hz, RMS Integrated Noise, RMS Time Jitter, and SSB Carrier/Noise options on the Legend menu. The blue integration-boundary cursors will be visible only if at least one of these options is selected for viewing. Like the Spot Cursor, the integration cursors automatically snap to their nearest vertical division.
Ctrl-right click to place the upper integration-range offset cursor used by the features above.
Important note: Like the single-point Spot Cursor, PN's trace-integration algorithm -- used whenever RMS noise, jitter, residual FM, or carrier/noise ratio values are displayed -- works on the displayed data after smoothing (if any) has been applied. This means that any changes you make to either the display resolution or smoothing level can affect the displayed values. Such effects are not usually very significant, but if repeatability is important, you may wish to make a note of the display resolution and smoothing level when logging your noise measurements.
Acquisition Dialog
Selecting a spectrum analyzer model from the Acquire menu will bring up the Acquisition dialog box. Depending on the analyzer type selected, the acquisition dialog's appearance can vary slightly from the example below.
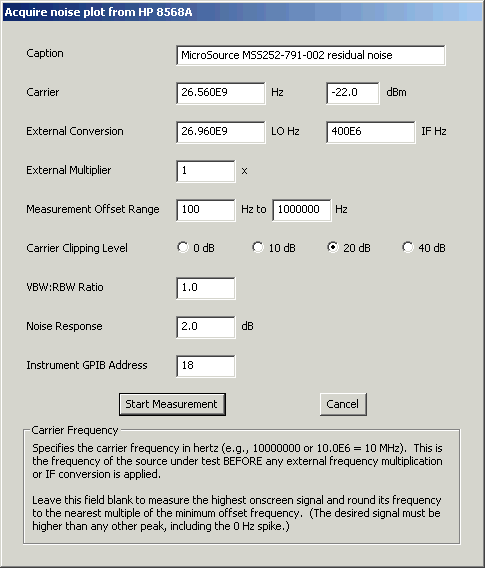
Caption specifies an optional caption for the trace being acquired. To display trace captions beneath the graph in the main window, select the Legend -> Trace option.
Carrier specifies the carrier frequency in hertz (e.g., 10000000 = 10 MHz). Scientific notation may also be used (e.g., 1.2E9 = 1.2 GHz). This is the frequency of the source under test, before any external frequency conversion or multiplication is applied.
With some analyzers, this field may be left blank to cause PN to select the highest onscreen signal for measurement. The desired signal must be higher than any other peak, including the 0-Hz spike if any. The selected frequency will be rounded to the nearest multiple of the minimum offset frequency.
You may also enter the carrier's amplitude level in dBm in the box to the right of the frequency field. This is the amplitude of the test signal as it arrives at the analyzer's input jack, after any external frequency conversion or multiplication is applied. You can leave this field blank with any analyzer model, but if the amplitude is known, specifying it here will reduce measurement time and improve repeatability.
The automatic carrier-detection feature is only as "smart" as the analyzer's marker functionality. It can fail to work properly if the 0-Hz spike or negative (mirrored) signals become visible while centering and zooming in on the desired signal.
External Conversion tells PN that the carrier is being mixed with an external LO signal to generate an IF within the spectrum analyzer's tuning range (or an optional frequency multiplier's input range). Both of these fields should be left blank if no external mixer is present. Otherwise, enter the LO frequency used to perform the conversion, followed by the IF at the mixer output where the measurement (or multiplication) takes place. More about indirect phase-noise measurements can be found in the FAQ.
External Multiplier tells PN that an external frequency multiplier (e.g., 2 for a doubler, 3 for a tripler...) is present at the spectrum analyzer�s RF input. Enter 1 here if no multiplier is present. Fractional values can be used to specify frequency division rather than multiplication (e.g., 0.125 for a divide-by-8 stage).
The use of an external xN multiplier improves the analyzer�s equivalent phase-noise floor by 20 x log10(N) dB. You can use a microwave "brick" source to multiply your test signal dozens of times if desired, but be sure you understand its loop-bandwidth and inband noise-peaking characteristics!
Measurement Offset Range specifies the minimum and maximum carrier offset frequencies in Hz. Offset frequencies are rounded to the nearest power of 10 and used to determine the left and right boundaries of the log-log plot.
The minimum offset frequency should be at least 3x the analyzer�s minimum resolution bandwidth, rounded up to the next decade. Minimum offsets below this limit will yield meaningless results. For instance, the Tektronix 494P's 30-Hz filter allows it to support minimum offsets down to 100 Hz, while the Tektronix 2782/2784's 3-Hz filter supports minimum offsets down to 10 Hz. Keep in mind, however, that the analyzer's filter skirt will have a pronounced effect on the trace if the requested minimum offset is not at least 10x the narrowest-available resolution bandwidth.
Most applications should specify 1 MHz as the maximum offset frequency.
Carrier Clipping Level specifies the amplitude offset above the analyzer�s reference level (top graticule line) at which the carrier will be positioned during the noise measurement. Clipping can improve the accuracy of measurements made near the analyzer�s LO or RF noise floor, at the risk of driving its front-end mixer into compression.
10 dB of clipping is recommended for most applications; 20 or 40 dB may be helpful on analyzers with 8-division displays such as the Tek 490 and HP 8590 series, or those with very low phase-noise floors such as the HP 8568A/B. The 40-dB option is also useful in suppressed- carrier measurements. Use caution at high signal levels!)
VBW:RBW Ratio specifies the video:resolution bandwidth ratio. This determines the compromise between measurement time and repeatability. Most applications will not need to change the default value of 1.0. Lower values can yield better repeatability � assuming the analyzer has warmed up thoroughly � but can take much longer to execute.
On some analyzers such as the Tektronix 490P/2750P series and HP 3588A/3589A, the VBW:RBW ratio is determined by the instrument's front-panel settings at the time the measurement is initiated.
Noise Response specifies the factor used to correct the measurement for the response of the analyzer�s RBW filters and video detector to Gaussian noise, plus any other system-level factors that require compensation. The noise-response value is added to all displayed data points.
PN's default noise-response value is 2 dB for many analyzers. Others, such as the Tektronix 490P/2750P and HP 3588A/3589A, maintain their noise-correction factors internally, so the default value for these instruments is 0 dB.
Instrument GPIB Address specifies the spectrum analyzer�s GPIB address as a decimal value. The default GPIB address for many of the HP analyzers supported by PN is 18.
Additional Instrument Notes
Tektronix 490P/2750P series The rear-panel LF-or-EOI switch must be set to '1' to use the GPIB Toolkit with all spectrum analyzer models in this series.
The earlier 492P and 496P analyzers do not use fully-synthesized tuning. As a result, you'll need to center the carrier signal manually prior to the beginning of each acquisition, even if you enter an explicit carrier frequency in the acquisition dialog. (The program will first tune the analyzer as close to the specified frequency as possible, so be sure to wait until you're prompted before you center the carrier.)
The 492P and 496P analyzers also don't compensate for errors in their IF center frequencies like the 494P and later models do, so accuracy in multi-decade measurements may be degraded.
HP 3585A/B Because the HP 3585A/B analyzers support only positive-peak detection, the VBW:RBW ratio in the Acquisition dialog should be set to 0.01 when high accuracy is required. This increases trace-acquisition time substantially, requiring up to 25 minutes for measurements between 10 Hz and 1 MHz. To speed up the acquisition process when absolute accuracy is not critical -- for example, when acquiring noise traces specifically for comparison with others from the same analyzer -- you can change the VBW:RBW default from 0.01 to 0.1 or even 1.0.
It is recommended that the HP 3585A/B's autoranging feature be turned off when using PN, especially when using carrier-clipping factors greater than 0 dB. (Use of carrier clipping may also cause the analyzer to report an overload condition; this is normal.) The REF LVL TRACK function should normally be left disabled.
Note that PN will disable auto-calibration and the error beeper while it is communicating with the HP 3585A/B, but it will not alter any other instrument settings, including autoranging and reference-level tracking, that are not directly associated with the measurement process.
Advantest R3264, R3267, and R3273 These analyzers can optionally use digital (FFT) filters to support resolution bandwidths down to 1 Hz. As a result, they are capable of PN acquisition at minimum offsets down to 10 Hz. However, their minimum offset is limited to 100 Hz (10 Hz RBW) unless digital filtering has been explicitly enabled with the Couple->RGB ≤100Hz ANLG/DGTL menu option.
By default, these digital filters are not enabled at power-up time; conventional analog filters are used instead. If you need to specify a 10-Hz minimum offset, you will need to enable the digital filters manually prior to beginning acquisition.
Due to ADC range limitations in the R3267 family, carrier clipping is ignored in spans acquired using the digital RBW filters.
Advantest R3132 series The default minimum offset with these analyzers is 10 kHz, corresponding to their standard 1-kHz minimum RBW filter setting. If your R3132-family analyzer has the optional 30-300 Hz RBW filters, you can specify minimum offsets down to 100 Hz.
Advantest R3131A It may be necessary to set write_delay_ms to 200 in the CONNECT.INI file (see below) when using a 2400-bps direct serial connection.
CONNECT.INI
The program directory should also contain a file called CONNECT.INI, which tells the GPIB Toolkit how to take advantage of various GPIB connectivity options. These include direct RS-232 or TCP/IP links, as well as the Prologix GPIB-USB and GPIB-LAN adapters.
If you have a Prologix adapter, you can review the comments in CONNECT.INI to learn how to configure PN and the other GPIB Toolkit applications to use it, or you can simply select your adapter in the Prologix configurator application (PROLOGIX.EXE) and press "Update CONNECT.INI" to automate the configuration process.
If the COM port specification in CONNECT.INI is commented out with a leading semicolon -- or if CONNECT.INI is missing entirely -- all GPIB Toolkit applications will attempt to communicate with the GPIB0 device via the National Instruments NI488.2 programming interface instead. This is the default behavior.
Note that some versions of Windows hide .INI file suffixes by default. In Windows 2000 and XP, for instance, CONNECT.INI may appear simply as "CONNECT," with the type "Configuration Settings." To turn off this behavior, go to the Tools->Folder Options->View tab in any Explorer window and deselect the "Hide file extensions for known file types" option.
Analyzer Baseline Traces
Different analyzer models have widely-varying system noise characteristics that must be taken into account when making direct phase-noise measurements. In particular, the source being measured needs to be at least a few dBc/Hz "dirtier" than the spectrum analyzer's own LO subsystem, or the resulting measurement will reveal more about the analyzer's noise profile than that of the source under test! To avoid drawing misleading conclusions from your noise measurements, it's a good idea to display them alongside a baseline plot for the analyzer model you're using.
The C:\Program Files\KE5FX\GPIB directory where PN.EXE is installed by default contains a subdirectory called Composite noise baseline plots. This subdirectory contains a variety of .PNP files that can be loaded and displayed by PN.EXE. These files are representative baseline noise-floor plots for various spectrum-analyzer models. If your analyzer model isn't included, it isn't difficult to make your own baseline plot, as long as you have access to a strong CW signal that's significantly cleaner than the analyzer's baseline response when tuned near the measurement frequency of interest.
In the manual for their HP 85671A noise-measurement package, Hewlett-Packard recommends against using the analyzer's own calibrator for noise baseline plots. The analyzer's LO and calibrator are both derived from the same internal source, potentially leading to correlation effects that misrepresent the analyzer's true noise response. In a pinch, though, your analyzer's calibrator is most likely OK as a noise-reference source. I haven't noticed any meaningful differences when comparing baseline traces taken from various analyzer models' calibrators versus known-uncorrelated sources.
How to Make Good Composite-Noise Measurements
First, read the HP app note cited near the top of this document. Then, read this help file in its entirety. Noise measurement can be tricky -- it's easy to fool yourself (and others) into thinking that bad data is valid.
One hint: watch the analyzer's trace while PN is working, and try to keep the noise floor out of both the top and bottom graticule divisions. Use 10 dB or 20 dB of carrier clipping if necessary to keep the noise floor above the bottom of the graticule where the analyzer's amplitude accuracy is at its worst. Especially when taking baseline plots, don't measure sources weaker than -20 dBm or so.
Don't forget that you may need to manually select 0 dB of RF attenuation at the analyzer's front panel to keep its front-end noise figure from dominating measurements of weaker signals. And don't forget how easy it is to blow mixer diodes when you do this.
Release Notes
Release 0.90 of 7-Aug-05
- Initial beta release for testing
Release 0.95 of 22-Aug-05
- Added HP 8560 and Tek 490/2750 support, plus some minor bug fixes and additional command-line options (/MIN, /MAX, /CLIP)
Release 0.96 of 5-Sep-05
- Moved command-line noise acquisition programs into the PNDRAW.EXE GUI shell, and renamed it PN.EXE
Release 1.00 of 13-Dec-05
- Removed references to HP 8566A/8567A/8568A analyzers. These models use a different set of GPIB control codes than the later 8566B/8567B/8568B instruments, and are not supported by versions of PN.EXE prior to 1.02
- Fixed a bug that could cause plots from Tektronix analyzers to be rendered with incomplete or broken traces
- Added Prologix GPIB-USB support
- Added ability to specify carrier amplitude explicitly to save measurement time and improve repeatability
- Caption text, if present, is now used to generate default filenames
- Fixed a bug that could cause cursor spot frequencies to be reported as off by one (e.g., 9999 Hz instead of 10000 Hz)
- Improved automatic carrier-frequency measurement on the HP analyzers
- Don't load more than 5 plots from the current working directory at startup time (in order to leave room on the screen for a newly-acquired one)
- Use 500-point acquisitions on Tek 490/2750 analyzers rather than 1000, for compatibility with older models
- Measure carrier level only in the first acquisition decade
- Don't issue RFATT? query on pre-1984 (492P/494P/496P) Tektronix analyzers
- Keep track of last directory used to save files, for easier use on Win98 machines
- Don't try to auto-detect debug monitor on parallel ports
- Added Acquire->Repeat last acquisition option
- Leave analyzer tuned to carrier frequency when finished with a sweep
- Added HTML user guide (this file)
- Windows desktop no longer used as the working directory when running from a desktop icon
- Clean up invalid .PNP files written during aborted acquisitions
- Fixed a bug that could cause the Spot Cursor to move during selection of menu options
- Added support for HP 8566A / 8567A / 8568A spectrum analyzers
- Added several trace-integration features
- Residual FM
- Jitter
- Total DSB integrated noise in degrees and radians
- SSB carrier/noise ratio in dB
- Fixed a bug that disabled the acquisition dialogs for the portable 8560-series analyzers
- Added a table marker in overlay mode to indicate the plot currently selected for browsing, saving or deletion
- Added keyboard accelerators to Smoothing menu
- RF attenuator state is now preserved properly during acquisition from HP 8566A / 8567A / 8568A analyzers
- Analyzer now returned to carrier*external multiplier at the end of acquisition, rather than carrier frequency itself
- Improved .PNP filename generation; fixed bug that could cause crashes with captions longer than 32 characters
- Table marker removed from printed/saved screen images
- Up/down arrow keys can now be used to select the next/previous plot for browsing, as alternatives to +/- keys
- HP 8590E-series analyzers now supported. Tested with HP 8596E; other 8590-series analyzers may or may not work
- Fixed minimum-offset bug introduced in post-1.05 slipstream update
- Added support for software-based GPIB address-selection feature in new Prologix adapter firmware
- Moved controller_mode, device_addressable, and host_addressable fields from 7470.INI to CONNECT.INI. These options now apply to all applications in the GPIB Toolkit, not just 7470.EXE.
- Added reset_to_local field to CONNECT.INI. This affects Prologix adapters only; see CONNECT.INI for more information
- HP 8568A rev-B spectrum analyzer successfully tested with new software-addressable Prologix adapter
- Fixed timer-overflow bug that could cause invalid sweep times to be reported
- Make sure HP analyzers are initialized in standard ASCII measurement-unit output format
- Always reset devices to local control at shutdown time when using NI-compatible GPIB interfaces
- HP 70000 series analyzers now supported. Tested with HP 70900A
- Serial ports beyond COM9 are now supported. Thanks to Bill Tracey, KD5TFD, for this patch!
- Added a workaround for noise-peaking at offsets near 20 kHz on HP 8566A/B analyzers. Data points in the 10 kHz-100 kHz decade are now acquired in 25-kHz spans instead of 100-kHz spans, and acquisition times are slightly longer as a result
- Added specific options for HP 8568A/B analyzers to the Acquire menu, since these models do not require the slower measurement procedure mentioned above
- Removed an obsolete option to detect noise-correction factors on the HP 8566-8568 analyzers
- Renamed Smoothing menu to Trace
- Added 24-, 48-, and 96-point smoothing options to the Trace menu; removed 128-point option
- Added Trace->Allow vertical clipping option
- Tweaked the graph-sizing algorithm to make better use of vertical space
- Changed trace-ghosting and graticule-contrast options to toggles
- Added Trace->Edit caption... dialog
- Improved automatic carrier-amplitude measurement on HP 8566-8568 analyzers
- Added the ability to specify an external IF conversion between the source under test and the spectrum analyzer or frequency multiplier
- Added the ability to specify noise-correction factors with all analyzers, including Tektronix 490P/2750P series
- Added the ability to specify fractional external-multiplication factors (i.e., frequency dividers between the source and analyzer)
- Issue FINE OFF command at beginning of acquisition from Tektronix 490P/2750P analyzers
- Tektronix 490P/2750P analyzers now work correctly with external frequency multipliers
- .PNP files are now reloaded at startup time
- Added confirmation dialog for file deletion
- The HP 8566A/B noise-peaking workaround from V1.15 is now optional, with an "Alternative Acquisition" checkbox in the acquisition dialog. This feature is turned off by default, because it can make the analyzer's baseline noise floor from 20 kHz-200 kHz appear worse. It also slows down acquisition, and it rarely improves the analyzer's 10 kHz-20 kHz baseline performance unless an outboard M/N synthesizer is used.
- Improved color fidelity in .GIF and .PCX files, particularly when saved at higher display resolutions
- Added support for the Tektronix 2782/2784 spectrum analyzers
- Increased the number of simultaneously-viewable plots from 6 to 8
- Allow the use of 3-Hz (Tektronix 2782/2784) and 30-Hz (Tektronix 494P) resolution bandwidths to achieve 10-Hz and 100-Hz minimum offsets, respectively
- HP 8566-8568 acquisition now uses the binary trace format for faster throughput. Total acquisition time is typically 20%-30% faster than in previous versions
- Added support for HP 3588A / HP 3589A spectrum analyzers
- Added support for Agilent E4400 series (tested on Agilent E4402B)
- Added support for HP 3585A/B spectrum analyzers
- Added 40-dB carrier-clipping option for use in suppressed-carrier measurements
- If a trace caption contains the substring (Broken trace), it will be rendered with a dashed line for improved legibility in black-and-white printouts
- To ensure visibility of heavily-filtered display traces, Trace->Allow vertical clipping is ignored if any visible plots have VBW:RBW ratios less than 1.0
- The most-recent directory where a file was loaded or saved is now remembered
- New code to center file dialogs within the main window
- Prompt before overwriting existing files with the Save command
- Added View->Move selected source up and View->Move selected source down commands (Ctrl-up-arrow and Ctrl-down-arrow, respectively) to allow reordering of displayed traces
- Added Trace->Enable spur reduction and Trace->Set spur threshold in dB... commands
- Added ctrl-keypad- and ctrl-keypad+ shortcuts for spur threshold adjustment
- Added Trace->Use alternate smoothing algorithm option
- Added Force 0 dB RF ATTEN option to HP 8566-8568 acquisition dialogs
- Assorted minor bug fixes and enhancements
- Improved rendering speed and responsiveness with trace cache
- Spur reduction is now applied prior to smoothing
- Invalidate trace cache when closing plots
- Elapsed measurement-time field (ELP) is now displayed as an arbitrary string rather than as an integer value in seconds
- Added View->Toggle visibility of selected source command (shortcut key v)
- Added support for the Advantest R3267 family of spectrum analyzers (R3264, R3267, and R3273)
- Added support for HP 4396A/B spectrum analyzers
- Acquisition from HP 8560/8590-series portables now uses binary transfers for faster throughput
- Disabled carrier clipping option on HP 4396A/B analyzers (causes overflow artifacts in DSP IF strip)
- HP 4395A/B support removed due to lack of SCPI compatibility
- Increased timeout interval for Prologix adapters during ASCII trace acquisition (which is now used only on HP 70000 series by default)
- Added Legend->Clip dB option to show the amount of carrier clipping requested when the plot was acquired
- Added support for the Advantest R3465 family of spectrum analyzers, including the R3463, R3465, R3263, and R3272 models
- All Advantest queries that follow commands flush the COM port buffer for better reliability with Prologix adapters
- RF attenuator settings on HP 3585A, 3588A, and 3589A reported as N/A, rather than 0 dB
- Automatic carrier-frequency measurement now uses counter marker on HP 8560A/B/E-series portables for improved accuracy
- Default carrier clipping level on Tektronix 490P/2750P-series analyzers raised from 10 dB to 20 dB for better accuracy with low-level signals
- Added File->Close all visible plots option (keyboard shortcut: Home)
- Acquired .PNP files are no longer saved in the Program Files subtree
- Renamed SERIAL.INI to CONNECT.INI, and added TCP/IP support
- Revised the Tektronix 490P/2750P code to support the original 492P and 496P analyzers. See the Tektronix 490P/2750P instrument notes above before using these models.
- Added support for the Advantest R3132 family of spectrum analyzers, including the R3132, R3162, R3172, and R3182 models
- Added support for the Advantest TR417x family of spectrum analyzers, including the TR4172
- Integration cursors are now labelled with their offsets on the graph in blue text, to save space in the legend table
- Added support for the Advantest R3261/R3361/R3265/R3271 family of spectrum analyzers
- Swapped yellow and cyan traces for better legibility
- HP 3585A/B trace acquisition is no longer interrupted by pressing the space bar in another application
- Clarified device support for E4400 and R&S FSE-series analyzers
- Added support for HP 4195A spectrum analyzer
- Added File->Export smoothed trace to .TXT or .CSV file ... option
- Added support for the Advantest R3131A spectrum analyzer
- Added support for Anritsu MS8604A
- Added File->Sort file dialogs by modification date option
- Added ability to load .PNP files with offsets down to 1 uHz, for use with Symmetricom TSC 5120A and similar analyzers
- Removed 'dBc/Hz' text from Y-axis scale values, added graph header caption
- Fixed bug introduced in 1.42 that could cause invalid integrated RMS noise readings
- Added support for Agilent E4406A VSA
Acknowledgements and Additional Notes
The assistance (and patience) of Dave Robinson, WW2R, and Vladan Temer of Sonoma Instrument, are gratefully acknowledged.
Thanks to Dr. Alfredo Rosati, I5UXJ for his contribution of the Tektronix 2782/2784 support code, Magnus Danielson for HP 4195A support, and Dmitry Teytelman for HP 4396A/B support. Advantest TR4172 code provided by Stefan Heinzmann. Ron Kittel, K8AQC, and Grant Hodgman, G8UBN provided extensive help with development and testing on the HP 3585A. Matt Ettus of Ettus Research provided access to the Advantest R3267, and Jack Smith, K8ZOA of Clifton Laboratories provided access to the Advantest R3463. Advantest R3131A support code was provided by Piotr Kaczmarzyk. Darren Storer, G7LWT provided access to the Advantest R3361A, while Dimitry Borzenko, 4Z5CP, provided access to the Anritsu MS8604A.
The assistance of Had Allhands, K7MLR with the HP 3588A, and of Abdul Nizar of Synapse Product Development with the Agilent E4402B, is greatly appreciated.
Released into the public domain 7-Aug-05 by John Miles, KE5FX.
Please contact jmiles@pop.net with feedback and enhancements!
Source code compilable with the free Microsoft Visual Studio Express package
No warranties, expressed or implied, are offered with this program.
Use at your own risk!
source:From: http://www.thegleam.com/ke5fx/gpib/pn.htm
0 comments:
Post a Comment